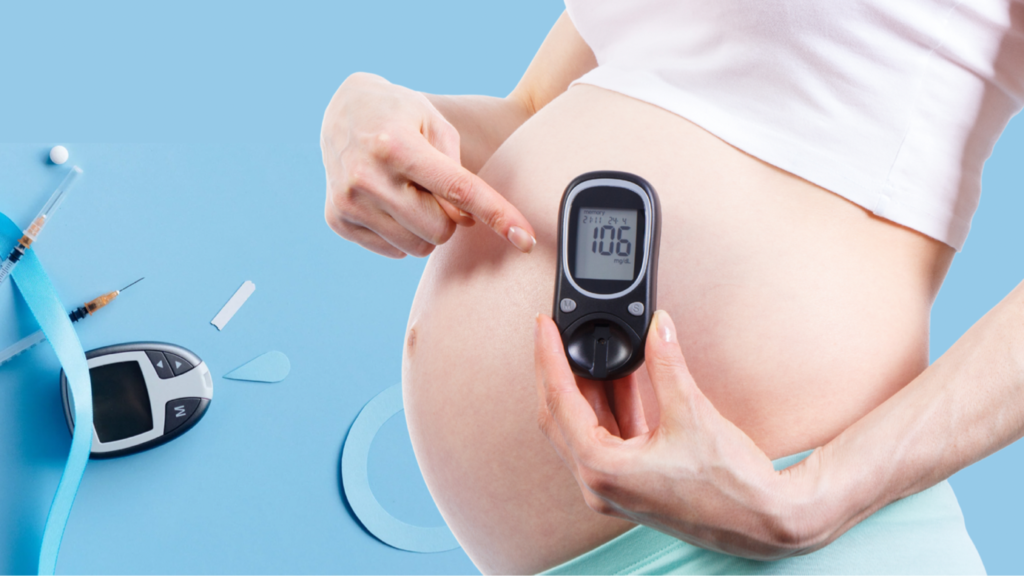
If a diabetic woman controls her blood sugar levels before and during pregnancy, she increases her chances of having a healthy baby. Controlling blood sugar also reduces the likelihood that a woman will develop common diabetes complications or that the complications will worsen during pregnancy.Here are a few steps how a diabetic woman can control her sugar levels:
- Consult your doctor as soon as possible
A pregnant woman with diabetes should see her doctor more frequently than a pregnant woman without diabetes. You and your doctor can work together to prevent or detect problems early.
- Consume Healthy Foods
Consume healthy foods from a diabetes-specific meal plan. A dietitian can assist you in developing a healthy meal plan. A dietitian can also teach you how to manage your blood sugar while pregnant.
- Regular exercise is essential
Another way to keep blood sugar under control is to exercise. It aids in the regulation of food intake. You can exercise regularly before, during, and after pregnancy after consulting with your doctor. Participate in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity five days per week. This could include brisk walking, swimming, or actively engaging in play with children.
- Take your pills and insulin exactly as directed
If your doctor prescribes diabetes pills or insulin, use them as directed to help keep your blood sugar under control.
- Quickly control and treat low blood sugar levels
Keeping blood sugar under control can occasionally result in low blood sugar. If you take diabetes pills or insulin, it’s a good idea to keep a source of quick sugar on hand at all times, such as hard candy, glucose tablets, or gel. It is also a good idea to teach family members, close coworkers, or friends how to assist in the event of a severe low blood sugar reaction.
- Frequently check your blood sugar
Because pregnancy changes the body’s need for energy, blood sugar levels can fluctuate rapidly. Your blood sugar should be checked frequently, as directed by your doctor. It is critical to understand how to adjust your food intake, exercise, and insulin based on the results of your blood sugar tests.
Why are regular doctor visits so critical for the mother and baby?
Doctor visits become very common during pregnancy, and these visits will almost certainly increase as the pregnancy progresses. As your child grows, your doctor will need to understand and consider several factors.
Is there a need for treatment, or do you need more medication? Do you require more rest or can you resume your normal activities? These are important questions, and any tests that your doctor orders are only because they are necessary.
What Is the Scope of FetoScan?
- First and foremost, a closer look at your baby
- The dimensions of the placenta
- The circulation of blood to the umbilical cord
- The quantity of amniotic fluid
When Is This Possible?
This is typically a third-trimester scan, but your doctor may order multiples. Don’t be concerned if this occurs. There are several reasons why you might require more growth scans than usual.
- If you have had a previous pregnancy that was difficult
- If you have had a previous C-Section, your doctor will examine the scar tissue. It is critical to understand and plan for the type of delivery
- If there are multiple babies (twins, triplets, etc.), additional growth scans may be required to assess their development
- If you have a history of gestational diabetes
- If your stomach is smaller or larger than expected
Measurements Obtained During The Scan
Before the scan begins, a few things are written down. One of them is your baby’s gestational age. This figure will provide average numbers, which can then be compared to determine whether or not your baby’s measurements are normal. The following are some of the key measurements taken during the scan:
Head measurements: There are two types of head measurements that are taken. The first is across the head, and the second is around it.
Abdomen: The circumference of your baby’s abdomen will also be measured during this scan.
Length of femur: It will be measured during this scan to assess the growth of the femur bone.
For the results to be released, these numbers are plotted on a graph and compared to the gestational age. The process calculates the estimated foetal weight.